Background
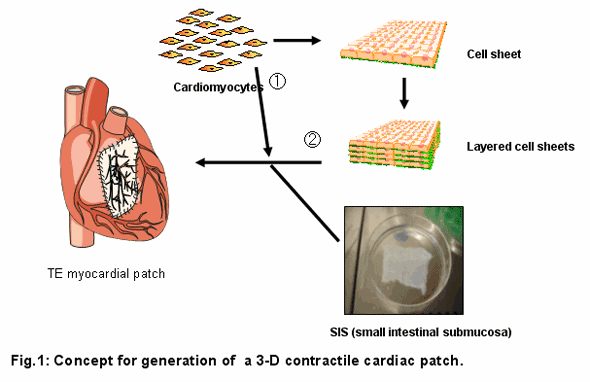
The availability of a contractile cardiac patch to replace or reinforce weakened heart tissue is of central interest for cardiologists or cardiac surgeons. Tissue engineering may offer possible solutions for these needs. By seeding neonatal rat cardiomyocytes on decellularized porcine small intestinal submucosa (SIS), a contractile construct with a defined contraction direction was generated. Here we report a second step towards an implantable myocardial patch, in such a way that cardiomyocyte sheets are combined with pre-seeded SIS constructs (Fig. 1).
Methods
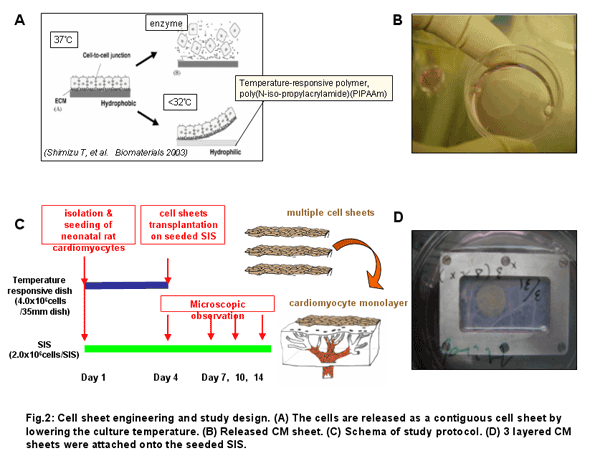
Porcine small intestinal submucosa (SIS) from which Serosa and Mucosa were mechanically removed, was decellularized with detergents, cut open along the longitudinal axis, fixed in a metal frame (2.5 x 4.5cm), and seeded onto the submucosa side with cardiomyocytes (CM) isolated from neonatal rat ventricles with Percoll gradient in a density of 1.8 x 105 CM/cm2. CM sheets were prepared using temperature-responsive dishes (UpCell; CellSeed, Tokyo, Japan; φ35mm) (Fig. 2A,B). 4.0 x 106 CM enriched by preplating were seeded onto a UpCell. Three days after CM seeding on SIS, 1 CM sheet (n=24) or 3 layered sheets (n=18) were stacked onto the pre-seeded SIS (Fig. 2D). Contraction of SIS and attached cell sheets was observed for additional 10 days. Histological analysis was also performed.
Results
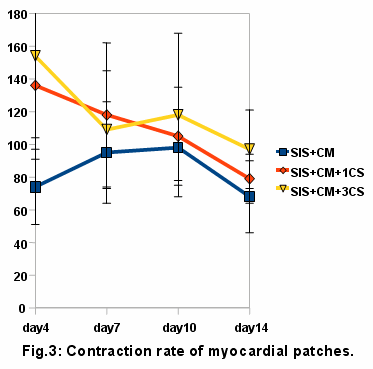
SIS seeded with CM started to contract spontaneously 2 days after seeding. After stacking the CM sheets, the constructs started to contract a few hour after adherence and their contraction was synchronized with the SIS contraction. Approximately 50% of myocardial patches (with 1 or 3 cell sheets) kept contracting until day 14. The beating rate of myocardial patches is shown in Fig. 3.
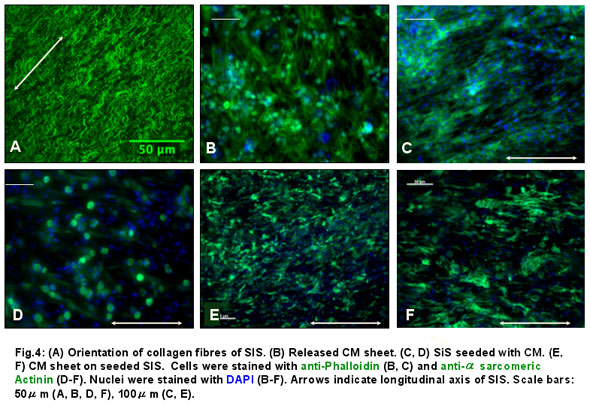
A large proportion of analyzed constructs showed a defined contraction direction parallel to the longitudinal axis of the SIS (seeded SIS: 83%; seeded SIS + 1 CM sheet: 70%; seeded SIS + 3 layered CM sheets: 71%, at day 7). This finding was in concordance with the histological finding of aligned CM parallel to the longitudinal axis of the SIS (Fig. 4).
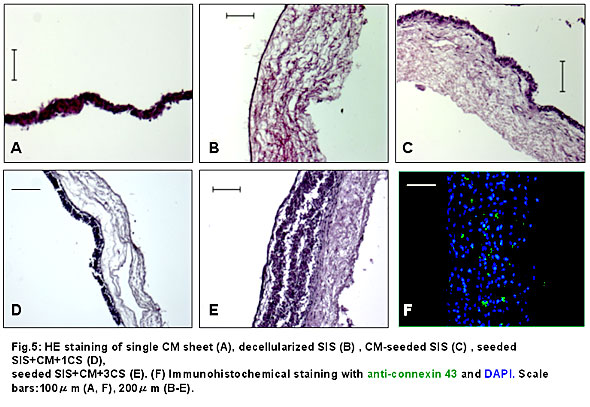
Cross-sectional observations with HE staining revealed that layered CM sheets had well adhered to seeded SIS. As to the thickness, a CM sheet was 40-50μm thick, SIS was 300-500μm thick and seeded SIS with 3 layered CM sheets was 600-800μm thick as a whole (Fig. 5A-E). Immunohistochemical study with an anti-connexin 43 antibody revealed diffuse gap junctions within the 3-layered CM sheets on seeded SIS (Fig. 5F).
Conclusion
By combining a reseeded, single CM layered matrix with CM sheets, a multiple layered contractile myocardial graft can be constructed that contracts in a defined direction. Such a graft may used surgically to support diseased myocardial tissue upon implantation, however, it may also represent an intermediate step on the way to a multiple layered, vascularized 3D contractile myocardial graft by means of biological vascularized matrix (BioVaM) and perfusionable bioreactor system.
Disclosure Statement: No competing financial interests exist.
Acknowledgements: This study was supported by grants from CORTISS Foundation, Japan Heart Foundation and the Uehara Memorial Foundation.
|